Model editor
Model editor tab allows a user to write de novo or modify existing code of a structural model.
Simurg is capable of parsing of various syntaxes, including MLXTRAN and rxode2, in addition to having its own flexible modeling language.
Import of an existing model from an external .txt file can be done by pressing  button.
Created or updated model can be saved to a file using
button.
Created or updated model can be saved to a file using  button.
button.
Essential strucutral elements of Simurg syntax
The only two mandatory sections that need to be present in a structural model file when using Simurg modeling syntax are # [INPUT] and # [MODEL], as shown on the figure:
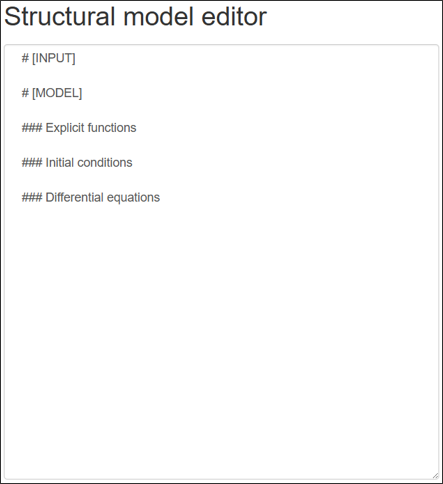
# [INPUT] contains the names and initial values of parameters to be estimated.
# [MODEL] contains the rest of the code, including fixed parameters, explicit functions, initial conditions, differential equations, etc.
Comments are introduced using # symbol. Thus, sections like ### Explicit functions or ### Initial conditions do not affect parsing and used for sorting the code.
End of the line should be marked with ;.
Syntax for the functional elements
Initial conditions
X(0) = X0, where X is a dependent variable, and X0 can be a number, a parameter, or an explicit function.
Differential equations
d/dt(X) = RHS, where X is a dependent variable, and RHS is the right hand side of a differential equation.
Bioavailability
f(X) = Fbio, where X is a dependent variable, and Fbio can be a number, a parameter, or an explicit function.
Lag time
Tlag(X) = Tlag, where X is a dependent variable, and Tlag can be a number, a parameter, or an explicit function.
Handling of covariates
If an object exists within model structure, but is not designated in # [INPUT], as explicit function, dependent variable or fixed parameter, it will be automatically treated as a covariate. Thus, model parsing at the Model tab will not fail as long as the modeling dataset contains a column with the name matching that of the object.
Example: 2-compartment PK model with first-order absorption

After defining the model, proceed to load it into the Model section.